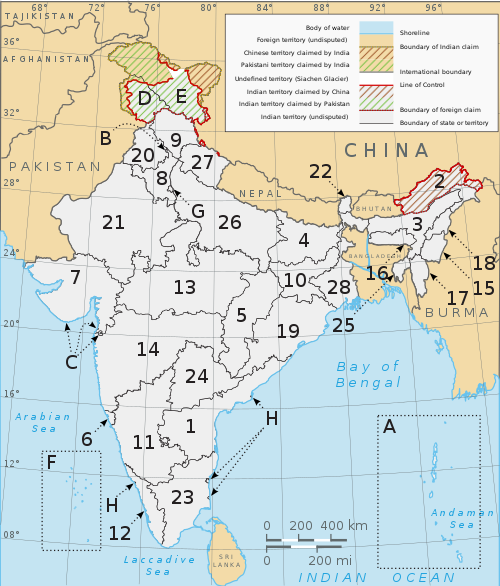
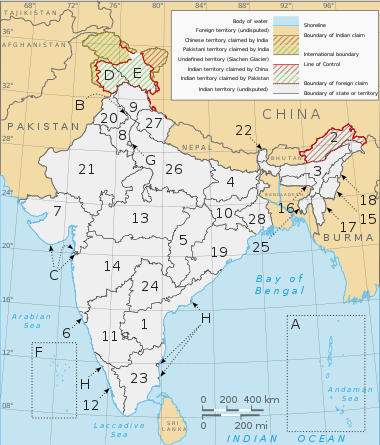
Administrative divisions of India
Thank you for being part of the Bharatpedia family! 0% transparency: ₹0 raised out of ₹100,000 (0 supporter) |
This article possibly contains original research. (August 2019) |
 |
|---|
| This article is part of a series on the politics and government of India |
The administrative divisions of India are subnational administrative units of India; they are composed of a nested hierarchy of country subdivisions.
Indian states and territories frequently use different local titles for the same level of subdivision (e.g., the mandals of Andhra Pradesh and Telangana correspond to tehsils of Uttar Pradesh and other Hindi-speaking states but to talukas of Gujarat, Goa, Karnataka, Kerala, Maharashtra, and Tamil Nadu).[1]
The smaller subdivisions (villages and blocks) exist only in rural areas. In urban areas, urban local bodies exist instead of these rural subdivisions.
Tiers of India[edit]
The diagram below outlines the six tiers of government:
Zones and regions[edit]
Zones[edit]
The states of India have been grouped into six zones having an Advisory Council "to develop the habit of cooperative working" among these States. Zonal Councils were set up vide Part-III of the States Reorganisation Act, 1956. The North Eastern States' special problems are addressed by another statutory body - The North Eastern Council, created by the North Eastern Council Act, 1971.[2] The present composition of each of these Zonal Councils is as under:[3]
- Northern Zonal Council, comprising Chandigarh, Delhi, Haryana, Himachal Pradesh, Jammu and Kashmir, Ladakh, Punjab, and Rajasthan;
- North Eastern Council, comprising Assam, Arunachal Pradesh, Manipur, Meghalaya, Mizoram, Nagaland and Tripura; The State of Sikkim has also been included in the North Eastern Council vide North Eastern Council (Amendment) Act, 2002 notified on 23 December 2002.[4]
- Central Zonal Council, comprising the States of Chhattisgarh, Madhya Pradesh, Uttarakhand and Uttar Pradesh;
- Eastern Zonal Council, comprising Bihar, Jharkhand, Odisha, and West Bengal;
- Western Zonal Council, comprising Dadra and Nagar Haveli and Daman and Diu, Goa, Gujarat, and Maharashtra;
- Southern Zonal Council, comprising Andhra Pradesh, Karnataka, Kerala, Puducherry, Tamil Nadu, and Telangana.
- Andaman and Nicobar Islands, Lakshadweep are not members of any of the Zonal Councils.[5] However, they are presently special invitees to the Southern Zonal Council[6]
Cultural zones[edit]
Each zone has a zonal headquarters where a zonal cultural center has been established.[7] Several states have membership in multiple zones, but no state subdivisions are utilized in the zonal divisions. In addition to promoting the culture of the zones they are responsible for, each zonal center also works to cross-promote and create exposure to other cultural zones of India by organizing functions and inviting artistes from other zones.
States and union territories[edit]
India is composed of 28 states and eight union territories (including a national capital territory).[15] The union territories are governed by administrators, appointed by the President of India. Three of these territories (Delhi, Jammu and Kashmir, Puducherry) have been given partial statehood, with elected legislatures and executive councils of ministers, with reduced powers.
States[edit]
| Number | State | Code | Estd. | Capital |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Andhra Pradesh | AP | Amaravati | |
| 2 | Arunachal Pradesh | AR | Itanagar | |
| 3 | Assam | AS | Dispur | |
| 4 | Bihar | BR | Patna | |
| 5 | Chhattisgarh | CG | Raipur[lower-alpha 1] | |
| 6 | Goa | GA | Panaji | |
| 7 | Gujarat | GJ | Gandhinagar | |
| 8 | Haryana | HR | Chandigarh (shared with Punjab, also a Union Territory) | |
| 9 | Himachal Pradesh | HP | Shimla (summer), Dharamshala (winter) | |
| 10 | Jharkhand | JH | Ranchi | |
| 11 | Karnataka | KA | Bangalore | |
| 12 | Kerala | KL | Thiruvananthapuram | |
| 13 | Madhya Pradesh | MP | Bhopal | |
| 14 | Maharashtra | MH | Mumbai (summer), Nagpur (winter) | |
| 15 | Manipur | MN | Imphal | |
| 16 | Meghalaya | ML | Shillong | |
| 17 | Mizoram | MZ | Aizawl | |
| 18 | Nagaland | NL | Kohima | |
| 19 | Odisha | OD | Bhubaneshwar | |
| 20 | Punjab | PB | Chandigarh (shared with Haryana, also a Union Territory) | |
| 21 | Rajasthan | RJ | Jaipur | |
| 22 | Sikkim | SK | Gangtok | |
| 23 | Tamil Nadu | TN | Chennai | |
| 24 | Telangana | TS | Hyderabad | |
| 25 | Tripura | TR | Agartala | |
| 26 | Uttar Pradesh | UP | Lucknow | |
| 27 | Uttarakhand | UT | Bhararisain (summer), Dehradun (winter) | |
| 28 | West Bengal | WB | Kolkata |
Union territories[edit]
| Letter / number | Union territory | Code | Capital |
|---|---|---|---|
| A | Andaman and Nicobar Islands | AN | Port Blair |
| B | Chandigarh | CH | Chandigarh (also the capital of Haryana and Punjab) |
| C | Dadra and Nagar Haveli and Daman and Diu | DD | Daman |
| D | Jammu and Kashmir | JK | Srinagar (summer), Jammu (winter) |
| E | Ladakh | LA | Leh and Kargil |
| F | Lakshadweep | LD | Kavaratti |
| G | National Capital Territory of Delhi | DL | New Delhi |
| H | Puducherry | PY | Pondicherry |
Autonomous administrative divisions[edit]
The Sixth Schedule of the Constitution of India allows for the formation of autonomous administrative divisions which have been given autonomy within their respective states.[16] Most of these autonomous areas are located in North East India.
Autonomous district councils operating under the Sixth Schedule of the Constitution of India are shown like this.[clarification needed]
Divisions[edit]
Many of the Indian states are subdivided into divisions, which have official administrative governmental status, and each division is headed by a senior IAS officer called Divisional Commissioner. Currently, superdistrict administrative divisions exist in 18 of the 28 states and 3 of the 8 union territories. The states of Gujarat, Kerala, Tamil Nadu, Andhra Pradesh, Telangana, Sikkim, Manipur, Tripura, Mizoram and Goa, and the union territories of Dadra and Nagar Haveli and Daman and Diu, Puducherry, Chandigarh, Lakshadweep and the Andaman and Nicobar Islands do not have divisions. Currently, there are a total of 102 divisions in India.
| State/Union Territory | Division | Headquarter District | Districts |
|---|---|---|---|
| Arunachal Pradesh | East | Namsai | Lohit, Anjaw, Tirap, Changlang, Lower Dibang Valley, Dibang Valley, East Siang, Upper Siang, Longding, Namsai, Siang |
| West | Lower Subansiri | Tawang, West Kameng, East Kameng, Papum Pare, Lower Subansiri, Kurung Kumey, Kra Daadi, Upper Subansiri, West Siang, Lower Siang and Itanagar Capital Complex | |
| Assam | Upper Assam Division | Jorhat | Charaideo, Dhemaji, Dibrugarh, Golaghat, Jorhat, Lakhimpur, Majuli, Sivasagar, and Tinsukia |
| Lower Assam Division | Guwahati | Baksa, Barpeta, Bongaigaon, Chirang, Dhubri, Goalpara, Nalbari, Kamrup Metropolitan, Kamrup Rural, Kokrajhar, and South Salmara-Mankachar | |
| North Assam Division | Tezpur | Biswanath, Darrang, Sonitpur, and Udalguri | |
| Central Assam Division | Nagaon | Dima Hasao, Hojai, East Karbi Anglong, West Karbi Anglong, Morigaon, and Nagaon | |
| Barak Valley | Silchar | Cachar, Hailakandi, and Karimganj | |
| Bihar | Patna division | Patna | Patna, Nalanda, Bhojpur, Rohtas, Buxar and Kaimur |
| Tirhut division | Muzaffarpur | West Champaran, East Champaran, Muzaffarpur, Sitamarhi, Sheohar and Vaishali | |
| Saran division | Chhapra | Saran, Siwan and Gopalganj | |
| Darbhanga division | Darbhanga | Darbhanga, Madhubani and Samastipur | |
| Kosi division | Saharsa | Saharsa, Madhepura and Supaul | |
| Purnia division | Purnia | Purnia, Katihar, Araria and Kishanganj | |
| Bhagalpur division | Bhagalpur | Bhagalpur and Banka | |
| Munger division | Munger | Munger, Jamui, Khagaria, Lakhisarai, Begusarai and Sheikhpura | |
| Magadh division | Gaya | Gaya, Nawada, Aurangabad, Jehanabad and Arwal | |
| Chhattisgarh | Surguja | Surguja | Koriya, Balrampur-Ramanujganj, Surajpur, Jashpur, Surguja and Mahendragarh |
| Bilaspur | Bilaspur | Bilaspur, Mungeli, Korba, Janjgir-Champa, Raigarh, Gourella Pendra Marwahi, Sarangarh-Bilaigarh, Sakti | |
| Durg | Durg | Kabirdham (Kawardha), Bemetara, Durg, Balod, Rajnandgaon, Mohla Manpur Chouki and Khairagarh | |
| Raipur | Raipur | Mahasamund, Baloda Bazar, Gariaband, Raipur and Dhamtari | |
| Bastar division | Bastar | Kanker (Uttar Bastar), Narayanpur, Kondagaon, Bastar, Dantewada (Dakshin Bastar), Bijapur and Sukma | |
| Haryana | Hisar division | Hisar | Fatehabad, Jind, Hisar and Sirsa |
| Gurgaon division | Gurugram | Gurugram, Mahendragarh and Rewari | |
| Ambala division | Ambala | Ambala, Kurukshetra, Panchkula and Yamuna Nagar | |
| Faridabad division | Faridabad | Faridabad, Palwal and Nuh | |
| Rohtak division | Rohtak | Jhajjar, Charkhi Dadri, Rohtak, Sonipat and Bhiwani | |
| Karnal division | Karnal | Karnal, Panipat and Kaithal | |
| Himachal Pradesh | Kangra | Kangra | Chamba, Kangra and Una |
| Mandi | Mandi | Bilaspur, Hamirpur, Kullu, Lahaul and Spiti and Mandi | |
| Shimla | Shimla | Kinnaur, Shimla, Sirmaur and Solan | |
| Jharkhand | Palamu division | Palamu | Garhwa, Latehar and Palamu |
| North Chotanagpur division | Hazaribagh | Bokaro, Chatra, Dhanbad, Giridih, Hazaribagh, Koderma and Ramgarh | |
| South Chotanagpur division | Ranchi | Gumla, Khunti, Lohardaga, Ranchi and Simdega | |
| Kolhan division | West Singhbhum | East Singhbhum, Seraikela Kharsawan district, and West Singhbhum | |
| Santhal Pargana division | Dumka | Godda, Deoghar, Dumka, Jamtara, Sahibganj and Pakur | |
| Karnataka | Bangalore division | Bangalore | Bangalore Urban, Bangalore Rural, Ramanagara, Chikkaballapur, Chitradurga, Davanagere, Kolar, Shivamogga and Tumakuru |
| Mysore division | Mysuru | Chamarajanagar, Chikkamagaluru, Udupi, Dakshina Kannada, Hassan, Kodagu, Mandya and Mysuru | |
| Belgaum division | Belagavi | Bagalkot, Belagavi, Vijayapura, Dharwad, Gadag, Haveri and Uttara Kannada | |
| Kalaburagi division | Kalaburagi |
Ballari, Bidar, Kalaburagi, Koppal, Raichur, Yadgir and Vijayanagara | |
| Madhya Pradesh | Bhopal division | Bhopal |
Bhopal, Raisen, Rajgarh, Sehore and Vidisha |
| Indore division | Indore |
Alirajpur district Barwani, Burhanpur, Indore, Dhar, Jhabua, Khandwa and Khargone | |
| Gwalior division | Gwalior |
Gwalior, Ashoknagar, Shivpuri, Datia and Guna | |
| Jabalpur division | Jabalpur | Balaghat, Chhindwara, Jabalpur, Katni, Mandla, Narsinghpur, Seoni and Dindori | |
| Rewa division | Rewa |
Rewa, Satna, Sidhi and Singrauli | |
| Sagar division | Sagar |
Chhatarpur, Damoh, Panna, Sagar, Tikamgarh and Niwari | |
| Shahdol division | Shahdol |
Anuppur, Shahdol and Umaria | |
| Ujjain division | Ujjain |
Agar Malwa, Dewas, Mandsaur, Neemuch, Ratlam, Ujjain and Shajapur | |
| Chambal division | Morena |
Morena, Sheopur and Bhind | |
| Narmadapuram division | Betul |
Betul, Harda and Hoshangabad | |
| Maharashtra | Amravati division | Amravati |
Akola, Amravati, Buldana, Yavatmal and Washim |
| Aurangabad division | Aurangabad |
Aurangabad Beed, Jalna, Osmanabad, Nanded, Latur, Parbhani and Hingoli | |
| Konkan division | Mumbai |
Mumbai City, Mumbai Suburban, Thane, Palghar, Raigad, Ratnagiri and Sindhudurg | |
| Nagpur division | Nagpur |
Bhandara, Chandrapur, Gadchiroli, Gondia, Nagpur and Wardha | |
| Nashik division | Nashik |
Ahmednagar, Dhule, Jalgaon, Nandurbar and Nashik | |
| Pune division | Pune |
Kolhapur, Pune, Sangli, Satara and Solapur | |
| Meghalaya | Tura | West Garo Hills |
South West Garo Hills, West Garo Hills, North Garo Hills, East Garo Hills and South Garo Hills |
| Shillong | East Khasi Hills |
West Khasi Hills, South West Khasi Hills, Ri-Bhoi, East Khasi Hills, West Jaintia Hills, and East Jaintia Hills | |
| Nagaland | Nagaland | Kohima |
Chümoukedima, Dimapur, Kiphire, Kohima, Longleng, Mokokchung, Mon, Niuland, Noklak, Peren, Phek, Shamator, Tseminyü, Tuensang, Wokha and Zünheboto |
| Odisha | Central | Cuttack |
Balasore, Bhadrak, Cuttack, Jagatsinghpur, Jajpur, Kendrapada, Khordha, Mayurbhanj, Nayagarh, and Puri |
| Northern | Sambalpur |
Angul, Balangir, Bargarh, Deogarh, Dhenkanal, Jharsuguda, Kendujhar, Sambalpur, Subarnapur and Sundargarh | |
| Southern | Berhampur |
Boudh, Gajapati, Ganjam, Kalahandi, Kandhamal, Koraput, Malkangiri, Nabarangpur, Nuapada and Rayagada | |
| Punjab | Patiala | Patiala |
Patiala, Sangrur, Malerkotla, Barnala, Fatehgarh Sahib and Ludhiana |
| Faridkot | Faridkot |
Faridkot, Bathinda and Mansa | |
| Firozepur | Firozepur |
Firozepur, Moga, Shri Muktsar Sahib and Fazilka | |
| Jalandhar | Jalandhar |
Jalandhar, Gurdaspur, Pathankot, Amritsar, Tarn Taran, Kapurthala and Hoshiarpur | |
| Rup Nagar | Rup Nagar |
Rup Nagar, Sahibzada Ajit Singh Nagar and Shaheed Bhagat Singh Nagar | |
| Rajasthan | Jaipur division | Jaipur |
Jaipur, Alwar, Jhunjhunu, Sikar and Dausa |
| Jodhpur division | Jodhpur |
Barmer, Jaisalmer, Jalore, Jodhpur, Pali and Sirohi | |
| Ajmer division | Ajmer |
Ajmer, Bhilwara, Nagaur and Tonk | |
| Udaipur division | Udaipur |
Udaipur, Banswara, Chittorgarh, Pratapgarh, Dungarpur and Rajsamand | |
| Bikaner division | Bikaner |
Bikaner, Churu, Sri Ganganagar and Hanumangarh | |
| Kota division | Kota |
Baran, Bundi, Jhalawar and Kota | |
| Bharatpur division | Bharatpur |
Bharatpur, Dholpur, Karauli, Sawai and Madhopur | |
| Uttar Pradesh | Agra division | Agra |
Agra, Firozabad, Mainpuri and Mathura |
| Aligarh division | Aligarh |
Aligarh, Etah, Hathras and Kasganj | |
| Ayodhya division | Ayodhya |
Ambedkar Nagar, Barabanki, Ayodhya, Sultanpur and Amethi | |
| Azamgarh division | Azamgarh |
Azamgarh, Ballia and Mau | |
| Bareilly division | Bareilly |
Badaun, Bareilly, Pilibhit and Shahjahanpur | |
| Basti division | Basti |
Basti, Sant Kabir Nagar and Siddharthnagar | |
| Chitrakoot division | Chitrakoot |
Banda, Chitrakoot, Hamirpur and Mahoba | |
| Devipatan division | Gonda |
Bahraich, Balarampur, Gonda and Shravasti | |
| Gorakhpur division | Gorakhpur |
Deoria, Gorakhpur, Kushinagar and Maharajganj | |
| Jhansi division | Jhansi |
Jalaun, Jhansi and Lalitpur | |
| Kanpur division | Kanpur Nagar |
Auraiya, Etawah, Farrukhabad, Kannauj, Kanpur Dehat and Kanpur Nagar | |
| Lucknow division | Lucknow |
Hardoi, Lakhimpur Kheri, Lucknow, Raebareli, Sitapur and Unnao | |
| Meerut division | Meerut |
Baghpat, Bulandshahar, Gautam Buddha Nagar, Ghaziabad, Meerut and Hapur | |
| Mirzapur division | Mirzapur |
Mirzapur, Sant Ravidas Nagar and Sonbhadra | |
| Moradabad division | Moradabad |
Bijnor, Amroha, Moradabad, Rampur and Sambhal | |
| Allahabad division | Allahabad |
Allahabad, Fatehpur, Kaushambi and Pratapgarh | |
| Saharanpur division | Saharanpur |
Muzaffarnagar, Saharanpur and Shamli | |
| Varanasi division | Varanasi |
Chandauli, Ghazipur, Jaunpur and Varanasi | |
| Uttarakhand | Kumaon division | Nainital |
Almora, Bageshwar, Champawat, Nainital, Pithoragarh and Udham Singh Nagar |
| Garhwal division | Pauri |
Chamoli, Dehradun, Haridwar, Pauri Garhwal, Rudraprayag, Tehri Garhwal and Uttarkashi | |
| West Bengal | Presidency division | Kolkata |
Howrah, Kolkata, Nadia, North 24 Parganas and South 24 Parganas |
| Medinipur division | Paschim Medinipur |
Bankura, Jhargram, Paschim Medinipur, Purba Medinipur and Purulia | |
| Malda division | Malda |
Dakshin Dinajpur, Malda, Murshidabad and Uttar Dinajpur | |
| Burdwan division | Hooghly |
Birbhum, Hooghly, Paschim Bardhaman and Purba Bardhaman | |
| Jalpaiguri division | Jalpaiguri |
Alipurduar, Cooch Behar, Darjeeling, Jalpaiguri and Kalimpong | |
| Delhi | Delhi division | Central Delhi |
Central Delhi, East Delhi, New Delhi, North Delhi, North East Delhi, North West Delhi, Shahdara, South Delhi, South East Delhi, South West Delhi and West Delhi |
| Jammu and Kashmir | Jammu Division | Jammu | Jammu, Doda, Kathua, Kishtwar, Poonch, Rajouri, Ramban, Reasi, Samba and Udhampur |
| Kashmir Division | Srinagar | Srinagar, Anantnag, Bandipora, Baramulla, Budgam, Ganderbal, Kulgam, Kupwara, Pulwama and Shopian | |
| Ladakh | Ladakh Division | Leh | Kargil and Leh |
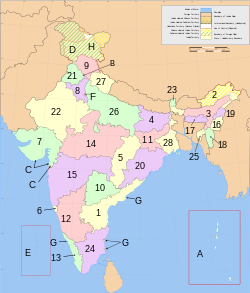
| Map key | Name of State or Union Territory (Italicized) | Number of Divisions | Population[17] | Population/district |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Andhra Pradesh | - | 49,386,799 | 3,798,985 |
| 2 | Arunachal Pradesh | 2 | 1,383,727 | 57,656 |
| 3 | Assam | 5 | 31,169,272 | 944,523 |
| 4 | Bihar | 9 | 104,099,452 | 2,739,459 |
| 5 | Chhattisgarh | 5 | 25,545,198 | 946,118 |
| 6 | Goa | - | 1,458,545 | 729,273 |
| 7 | Gujarat | - | 60,439,692 | 1,831,506 |
| 8 | Haryana | 6 | 25,351,462 | 1,152,339 |
| 9 | Himachal Pradesh | 3 | 6,864,602 | 572,050 |
| 10 | Telangana | - | 35,193,978 | 1,135,290 |
| 11 | Jharkhand | 5 | 32,988,134 | 1,374,506 |
| 12 | Karnataka | 4 | 61,095,297 | 2,036,510 |
| 13 | Kerala | - | 33,406,061 | 2,386,147 |
| 14 | Madhya Pradesh | 10 | 72,626,809 | 1,396,669 |
| 15 | Maharashtra | 6 | 112,374,333 | 3,121,509 |
| 16 | Manipur | - | 2,721,756 | 170,110 |
| 17 | Meghalaya | 2 | 2,966,889 | 269,717 |
| 18 | Mizoram | - | 1,097,206 | 137,151 |
| 19 | Nagaland | 1 | 1,978,502 | 179,864 |
| 20 | Odisha | 3 | 41,974,218 | 1,399,141 |
| 21 | Punjab | 5 | 27,743,338 | 1,261,061 |
| 22 | Rajasthan | 7 | 68,548,437 | 2,077,225 |
| 23 | Sikkim | - | 610,577 | 152,644 |
| 24 | Tamil Nadu | - | 72,147,030 | 2,254,595 |
| 25 | Tripura | - | 3,673,917 | 459,240 |
| 26 | Uttar Pradesh | 18 | 199,812,341 | 2,664,165 |
| 27 | Uttarakhand | 2 | 10,086,292 | 775,869 |
| 28 | West Bengal | 5 | 91,276,115 | 3,968,527 |
| A | Andaman and Nicobar Islands | - | 380,581 | 126,860 |
| B | Chandigarh | - | 1,055,450 | 1,055,450 |
| C | Dadra and Nagar Haveli and Daman and Diu | - | 586,956 | 195,652 |
| D | Jammu and Kashmir | 2 | 12,258,433 | 612,922 |
| E | Lakshadweep | - | 64,473 | 64,473 |
| F | Delhi | 1 | 16,787,941 | 1,526,176 |
| G | Puducherry | - | 1,247,953 | 311,988 |
| H | Ladakh | 1 | 290,492 | 145,246 |
| 36 | Total | 102 | 1,210,854,977 | 1,677,084 |
| valign="top" width="300px" |
|}
Regions within states[edit]
Some states consist of regions, which have no official administrative governmental status. They are purely geographic regions; some correspond to historic countries, states or provinces. A region may comprise one or more divisions, averaging about three divisions per region. However, the boundaries of the regions and the boundaries of the divisions do not always coincide exactly. So far there has been no movement to give the regions official administrative status. If this was to be done, it would presumably require that the boundaries of the regions be slightly modified so that they correspond exactly with their constituent districts.
Districts[edit]
States and territories (or divisions) are further subdivided into districts (zilla), of which there are 775 (as of 2022). Each District is headed by an IAS officer called District Magistrate.
|
Subdistricts[edit]
Tehsils, talukas, subdivisions, mandals, circles, headed by a Tehsildar or Talukdar or MRO, comprise several villages or village clusters. The governmental / elected bodies at the tehsil level are called the Panchayat samiti.
States use varying names for their subdistricts.[18]
| State | Type | Count |
|---|---|---|
| Andhra Pradesh | Mandal | 664[19] |
| Arunachal Pradesh | Circle | 149 |
| Assam | Subdivision | 155 |
| Bihar | Subdivision | 101 |
| Chhattisgarh | Tehsil | 149 |
| Goa | Taluka | 12 |
| Gujarat | Taluka | 248 |
| Haryana | Tehsil | 67 |
| Himachal Pradesh | Tehsil | 109 |
| Jharkhand | Subdivision | 210 |
| Karnataka | Taluka | 206 |
| Kerala | Taluka | 77 |
| Madhya Pradesh | Tehsil | 367 |
| Maharashtra | Taluka | 353 |
| Manipur | Subdivision | 38 |
| Meghalaya | Subdivision | 39 |
| Mizoram | Subdivision | 22 |
| Nagaland | Circle | 93 |
| Odisha | Tehsil | 485 |
| Punjab | Tehsil | 72 |
| Rajasthan | Tehsil | 268 |
| Sikkim | Subdivision | 9 |
| Tamil Nadu | Taluka | 201 |
| Telangana | Mandal | 452 |
| Tripura | Subdivision | 38 |
| Uttar Pradesh | Tehsil | 350 |
| Uttarakhand | Tehsil | 113 |
| West Bengal | Subdivision | 69 |
| Union Territory | Type | Count |
|---|---|---|
| Andaman and Nicobar Islands | Tehsil | 7 |
| Chandigarh | Tehsil | 1 |
| Dadra and Nagar Haveli and Daman and Diu | Taluka | 3 |
| Delhi | Tehsil | 33 |
| Jammu and Kashmir | Tehsil | 55 |
| Ladakh | Tehsil | 4 |
| Lakshadweep | Subdivision | 4 |
| Puducherry | Commune Panchayat | 10 |
Rural level[edit]
Blocks[edit]
The Community Development Block also known as CD Block or just block, is often the next level of administrative division (for development purposes, whereas tehsil is next to the district for revenue purposes).
| State | CD Block | Number of CD Blocks |
|---|---|---|
| Bihar | CD Block | 534 |
| Haryana | CD Block | 140 |
| Jharkhand | CD Block | 263[20] |
| Tripura | CD Block | 58 |
| Uttarakhand | CD Block | 95 |
| West Bengal | CD Block | 341[21] |
Villages[edit]
Villages are often the lowest level of subdivisions in India. The governmental bodies at the village level are called Gram Panchayat, of which there were an estimated 256,000 in 2002. Each Gram Panchayat covers a large village or a cluster of smaller villages with a combined population exceeding 500 Gram Sabha. Clusters of villages are also sometimes called Hobli or Patti.
Habitations[edit]
Certain governmental functions and activities - including clean water availability, rural development, and education - are tracked at a sub-village level.[22] These hamlets are termed "habitations". India is composed of 1,714,556 habitations [23] In some states, most villages have a single habitation; in others (notably Kerala and Tripura) there is a high ratio of habitations to villages.[24]
Metropolitan area[edit]
A metro area usually comprises multiple jurisdictions and municipalities: neighbourhoods, townships, cities, exurbs, suburbs, counties, districts, states, and even nations like the eurodistricts. As social, economic, and political institutions have changed, metropolitan areas have become key economic and political regions. Metropolitan areas include one or more urban areas, as well as satellite cities, towns, and intervening rural areas that are socio-economically tied to the urban core, typically measured by commuting patterns The metropolitan cities of India are: Mumbai, Delhi, Kolkata, Chennai, Bangalore, Hyderabad, Ahmedabad and Pune.
Historic[edit]
See also[edit]
- States and union territories of India
- Autonomous administrative divisions of India
- Cultural Zones of India
Notes[edit]
- ↑ Naya Raipur is planned to replace Raipur as the capital city of Chhattisgarh.
References[edit]
- ↑ "Archived copy - Table 1.1 - India at a Glance - Administrative Division - 2001" (PDF). Office of the Registrar General of India, New Delhi. Archived from the original (PDF) on 24 September 2015. Retrieved 18 August 2018.
- ↑ "Archived copy". Archived from the original on 15 April 2012. Retrieved 25 March 2012.
{{cite web}}: CS1 maint: archived copy as title (link) - ↑ "Archived copy". Archived from the original on 8 May 2012. Retrieved 7 March 2012.
{{cite web}}: CS1 maint: archived copy as title (link) - ↑ "Zonal Council |". mha.nic.in. Archived from the original on 12 May 2017. Retrieved 26 October 2016.
- ↑ "The States Reorganisation Act, 1956 (Act No.37 Of 1956) Part – Iii Zones And Zonal Councils" (PDF). Interstatecouncil.nic.in. Retrieved 27 December 2017.
- ↑ "Present Composition Of The Southern Zonal Council" (PDF). Interstatecouncil.nic.in. Retrieved 27 December 2017.
- ↑ South Zone Culture Center: Other Zones, South Zone Culture Centre, retrieved 15 December 2010,
... North East Zone Cultural Centre – Nagaland – Assam, Tripura, Manipur, Arunachal Pradesh, Nagaland & Meghalaya ...
- ↑ "Inauguration of SĀDHANĀ". szccindia.org. Retrieved 22 November 2021.
- ↑ "Application for solo exhibition at Raja Ravi Verma Art gallery, Nagpur" (docx). South Central Zone Cultural Center. p. 4. Retrieved 25 May 2017.[permanent dead link]
- ↑ "North Zone Cultural Centre". culturenorthindia. Retrieved 22 November 2021.
- ↑ "NCZCC – North Central Zone Cultural Centre, Prayagraj, Uttar Pradesh". nczcc. Retrieved 22 November 2021.
- ↑ "Eastern Zonal Cultural Centre". www.ezcc-india.org. Archived from the original on 15 January 2022. Retrieved 22 November 2021.
- ↑ "North East Zonal Cultural Centre". www.nezccindia.org.in. Retrieved 22 November 2021.
- ↑ "About West Zone Cultural Center – WZCC – West Zone Cultural Centre". wzccindia.com. Retrieved 22 February 2022.
- ↑ "Profile | National Portal of India". www.india.gov.in. Retrieved 31 March 2020.
- ↑ "Sixth Schedule" (PDF). Archived (PDF) from the original on 27 October 2019.
- ↑ 17.0 17.1 "Population and decadal change by residence : 2011 (PERSONS)" (PDF). Office of the Registrar General & Census Commissioner, India. p. 2. Archived from the original (PDF) on 24 June 2016. Retrieved 15 January 2019.
- ↑ "Statement showing the Nomenclature and Number of Sub-Districts in States/UTs". Office of The Registrar General & Census Commissioner, India, New Delhi. 2010–2011. Retrieved 3 October 2011.
- ↑ "List of Mandals" (PDF). msmehyd.ap.nic.in. Andhra Pradesh State. Archived from the original (PDF) on 11 September 2016. Retrieved 3 September 2016.
- ↑ "Names of Blocks of Jharkhand". Jharkhandi Baba. 21 October 2017. Archived from the original on 21 October 2017. Retrieved 21 October 2017.
- ↑ "Census India, West Bengal" (PDF). Retrieved 20 April 2020.
- ↑ Indian Department of Drinking Water Supply Archived 21 July 2011 at the Wayback Machine
- ↑ "National Habitation Survey 2003". Archived from the original on 21 July 2011.
- ↑ Indian Department of Education Archived 21 July 2011 at the Wayback Machine