Mundari language
It has been suggested that this article be split into a new article titled Mundari Bani Hisir. (Discuss) (May 2021) |
| Mundari | |
|---|---|
| मुंडारी, মুন্ডারি, ମୁଣ୍ଡାରୀ | |
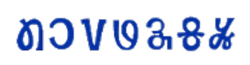 'Mundari' in Mundari Bani script | |
| Native to | India, Bangladesh, Nepal |
| Ethnicity | Munda, Bhumij |
Native speakers | 1,661,656 (2011 census)[1] |
Austroasiatic
| |
| Dialects |
|
| Mundari Bani, others: Odia, Devanagari, Bengali, Latin | |
| Official status | |
Official language in |
|
| Language codes | |
| ISO 639-3 | unr |
| Glottolog | mund1320 |
Mundari (Munɖari) is a Munda language of the Austroasiatic language family spoken by the Munda tribes in eastern Indian states of Jharkhand, Odisha and West Bengal. It is closely related to Santali. Mundari Bani,[2] a script specifically to write Mundari, was invented by Rohidas Singh Nag.[3][4] It has also been written in the Devanagari, Odia, Bengali, and Latin writing systems.
History[edit | edit source]
According to linguist Paul Sidwell (2018), Munda languages probably arrived on coast of Odisha from Indochina about 4000–3500 years ago and spread after Indo-Aryan migration to Odisha.[5]
Geographical distribution[edit | edit source]
Mundari is spoken in the Ranchi, Khunti, Seraikela Kharsawan and West Singhbhum, East Singhbhum district of Jharkhand, and in the Mayurbhanj, Kendujhar, Baleshwar, Sundargarh district of Odisha by at least 1.1 million people.[6] Another 500,000, mainly in Odisha and Assam, are recorded in the census as speaking "Munda," potentially another name for Mundari.
Dialects[edit | edit source]
Toshiki Osada (2008:99), citing the Encyclopaedia Mundarica (vol. 1, p. 6), lists the following dialects of Mundari, which are spoken mostly in Jharkhand state.
- Hasada ([hasa-daʔ]): east of the Ranchi-Chaibasa Road
- Naguri ([naguri]): west of the Ranchi-Chaibasa Road
- Tamaria ([tamaɽ-ia]) or Latar: Panchpargana area (Bundu, Tamar, Silli, Baranda, and Rahe)
- Kera ([keraʔ]): ethnic Oraon who live in the Ranchi city area
Bhumij, listed in many sources as a separate language, may in fact be a variety of the Latar (Tamaria) dialect of Mundari. It is spoken across Jharkhand state and in Mayurbhanj district, Odisha (Anderson 2008:196). There may be around 50,000 Bhumij speakers, although the census records around 27,000.[7]
Phonology[edit | edit source]
The phonology of Mundari is similar to the surrounding closely related Austroasiatic languages but considerably different from either Indo-Aryan or Dravidian. Perhaps the most foreign phonological influence has been on the vowels. Whereas the branches of Austroasiatic in Southeast Asia are rich in vowel phonemes, Mundari has only five. The consonant inventory of Mundari is similar to other Austroasiatic languages with the exception of retroflex consonants, which seem to appear only in loanwords. (Osada 2008)
Vowels[edit | edit source]
Mundari has five vowel phonemes. All vowels have long and short as well as nasalized allophones, but neither length nor nasality are contrastive. All vowels in open monosyllables are quantitatively longer than those in closed syllables, and those following nasal consonants or /ɟ/ are nasalized. Vowels preceding or following /ɳ/ are also nasalized.
| Front | Central | Back | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Close | i | u | |
| Mid | e | o | |
| Open | a |
Consonants[edit | edit source]
Mundari's consonant inventory consists of 23 basic phonemes. The Naguri and Kera dialects include aspirated stops as additional phonemes, here enclosed in parentheses.
| Labial | Dental | Retroflex | Palatal | Velar | Glottal | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Stop | voiceless | p | t̪ | ʈ | t͡ɕ | k | ʔ |
| aspirated | (pʰ) | (t̪ʰ) | (ʈʰ) | (t͡ɕʰ) | (kʰ) | ||
| voiced | b | d̪ | ɖ | d͡ʑ | g | ||
| Fricative | s̪ | h | |||||
| Nasal | m | n̪ | ɳ | ɲ | ŋ | ||
| Approximant | w | l | ɽ | j | |||
| Trill | r | ||||||
Counting[edit | edit source]
| Mundari | Transliteration | Translation |
|---|---|---|
| मिसा | Missa | Once |
| बरसा | Birsa | Twice |
| अपिसा | Apisa | Thrice |
| उपनुसा | Upnisa | four times |
| मोंड़ेसा | Mondesa | Five times |
| तुरिसा | Turisa | Six times |
| ए'सा | Eh sa | Seven times |
| इरलसा | Erklsa | Eight Times |
| अरे-सा | Are sa | Nine times |
| गेलसा | Gelsa | Ten times |
| Gel Miyad | ... | Eleven |
| Gel Bariya | ... | Twelve |
| , Apiya | ... | Thirteen |
| , Upuna | ... | Fourteen |
| , Modeya | ... | Fifteen |
| , Turiya | ... | Sixteen |
| , Eya | ... | Seventeen |
| , Iriliya | ... | Eighteen |
| , Areya | ... | Nineteen |
| Mid Hisi | ... | Twenty |
| Hisi Miyad | ... | Twenty-one |
| Mid hisi Gel | ... | Thirty |
| Hisi Gel Miyad | ... | Thirty-one |
| Bar Hisi | ... | Forty |
| Bar Hisi Miyad | ... | Forty-one |
| Bar Hisi Gel | ... | Fifty |
| Aapi Hisi | ... | Sixty |
| Aapi Hisi Gel | ... | Seventy |
| Upun Hisi | ... | Eighty |
| Upun Hisi Gel | ... | Ninety |
| Mid Saaye | ... | One hundred |
| Bar Saaye | ... | Two hundred |
| Mid Hazar | ... | One thousand |
| Mid Lak | ... | One lakh |
Relations[edit | edit source]
| Mundari | Transliteration | Translation |
|---|---|---|
| ऐंन्गा | Enga | Mother |
| आपूम | Apum | Father |
| हग्गा | Hagga | Brother |
| मिस्सी | Missi | Sister |
| गुया | Guya | Sister/brother of sister/brother in law |
| गतिंग | Gatin | Friend |
| Hon koda | ... | Son |
| Hon Kudi | ... | Daughter |
Verb[edit | edit source]
| Mundari | Transliteration | Translation |
|---|---|---|
| रिकाएआ | Rikā'ē'ā | Does |
| ओलेआ | Ol'ē'ā | Write |
| जगरेआ | Jagor'ē'ā | Talk |
| पढ़वएआ | Padv'ē'ā | Read |
| लेलेआ | Lel'ē'ā | Look / see |
| सेनेआ | Sen'ē'ā | Come along with |
| नमेआ | Nem'ē'ā | Found |
| निरेआ | Nir'ē'ā | Run |
| सबेआ | Sab'ē'ā | Hold |
| लेका एआ | Leka'ē'ā | Count |
| मुकाएआ | Muka'ē'ā | Measure |
| रिका एआ | Rika'ē'ā | Cut |
| Hedem | ... | Sweet |
| Kete-e | ... | Hard |
| Lebe-e | ... | Soft |
| Singi | ... | Sun |
| Chandu-u | ... | Moon |
| Ipil | ... | Stars |
| Sirma | ... | Sky |
| Ote Dishum | ... | Earth |
| Rimil | ... | cloud |
| Hoyo | ... | Air/Wind |
| Gitil | ... | Sands |
| Dhudi | ... | Dust |
| Losod | ... | Muddy |
| Hodomo | ... | Body |
| Tasad | ... | Grass |
| Daru | ... | Tree |
| Sakam | ... | Leaf |
| Dayir | ... | Branches of Tree |
Writing system[edit | edit source]
Mandari is also written in native Mundari Bani, invented in the 1980s by Rohidas Singh Nag.
References[edit | edit source]
- ↑ "Statement 1: Abstract of speakers' strength of languages and mother tongues – 2011". www.censusindia.gov.in. Office of the Registrar General & Census Commissioner, India. Retrieved 7 July 2018.
- ↑ "Mundari Bani".
- ↑ "BMS to intensify agitation on Mundari language". oneindia.com. Retrieved 4 April 2018.
- ↑ "Adivasi. Volume 52. Number 1&2. June&December 2012". Page 22
- ↑ Sidwell, Paul. 2018. "Austroasiatic Studies: state of the art in 2018". Presentation at the Graduate Institute of Linguistics, National Tsing Hua University, Taiwan, May 22, 2018.
- ↑ "Mundari". ethnologue.
- ↑ "Keeping Munda in mind". Pune Mirror. Retrieved 4 April 2018.
- Anderson, Gregory D.S (ed). 2008. The Munda languages. Routledge Language Family Series 3.New York: Routledge. ISBN 0-415-32890-X.
- Osada Toshiki. 2008. "Mundari". In Anderson, Gregory D.S (ed). The Munda languages, 99–164. Routledge Language Family Series 3.New York: Routledge. ISBN 0-415-32890-X.
8.https://omniglot.com/writing/mundaribani.htm 9.https://omniglot.com/writing/mundari.htm
Further reading[edit | edit source]
- Evans, Nicholas & Toshki Osada. 2005a. Mundari: the myth of a language without word classes. In Linguistic Typology 9.3, pp. 351–390.
- Evans, Nicholas & Toshki Osada. 2005b. Mundari and argumentation in word-class analysis. In Linguistic Typology 9.3, pp. 442–457
- Hengeveld, Kees & Jan Rijkhoff. 2005. Mundari as a flexible language. In Linguistic Typology 9.3, pp. 406–431.
- Newberry, J. (2000). North Munda dialects: Mundari, Santali, Bhumia. Victoria, B.C.: J. Newberry. ISBN 0-921599-68-4
Texts[edit | edit source]
- Johann Hoffmann (1903). Mundari grammar. Bengal Secretariat Press. Retrieved 25 August 2012.
- J. C. Whitley (1873). A Mundári Primer. Bengal Secretariat Press. Retrieved 25 August 2012.
- Carl Gustav Rudolph Eduard Alfred Nottrott (1882). Grammatik der Kolh-Sprache. Gütersloh: Druck von C. Bertelsmann. Retrieved 25 August 2012.
- Four gospels in Mundari. Bible Society. 1881. Retrieved 25 August 2012.
External links[edit | edit source]
- Mundari Bibliography at Department of Linguistics, University of Osnabrueck, Germany
- Detailed language map of eastern Nepal, see language #68 in green along eastern border
- http://projekt.ht.lu.se/rwaai RWAAI (Repository and Workspace for Austroasiatic Intangible Heritage)
- http://hdl.handle.net/10050/00-0000-0000-0003-A6AA-C@view Mundari language in RWAAI Digital Archive
