Medak district
Medak district | |
|---|---|
 Paddy fields in Medak | |
| Country | India |
| State | Telangana |
| Headquarters | Medak |
| Tehsils | 7 |
| Government | |
| • District collector | Sri Dharma Reddy |
| Population (2011) | |
| • Total | 767,428 |
| Time zone | UTC+05:30 (IST) |
| Website | medak |
Medak district is a district located in the Indian state of Telangana. Medak is the district headquarters.[1] The district shares boundaries with Sangareddy, Kamareddy, Siddipet and Medchal districts.
History[edit]
Traces of Neolithic and Megalithic culture was found at Edithanur and Wargal[2] village hillocks in the district. Rock paintings were found at Edithanur boulders[3] and Hastallapur rocks.[4]
Nizam state[edit]
In 20th century Medak district was a part of Nizam princely State before independence and merged into Hyderabad State in Independent India and presently a district of Telangana. Qutub Shahis named it as Gulshanabad which means '"city of gardens'" due to its luscious greenery.
Geography[edit]
The district is spread over an area of 2,740.89 square kilometres (1,058.26 sq mi).[5]
Demographics[edit]
[needs update] As of the 2011 Census of India, the district has a population of 767,428.[5]
Economy[edit]
In 2006 the Indian government named Medak one of the country's 250 most backward districts (out of a total of 640).[6] It is one of the thirteen districts in Andhra Pradesh currently receiving funds from the Backward Regions Grant Fund Programme (BRGF).[6]
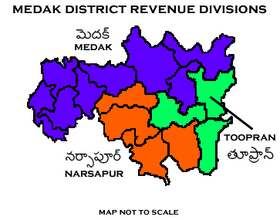
Administrative divisions[edit]
The district is divided into three revenue divisions of Medak, Narsapur and Tupran. These are sub-divided into sixteen mandals and has 381 villages.[5] Dharma Reddy is the present collector of the district.[7]
Mandals[edit]
The below table categorizes 16 mandals into their respective revenue divisions in the district:[8]
| S.No. | Medak revenue division | Narsapur revenue division | Tupran revenue division |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Medak | Narsapur | Ramayampeta |
| 2 | Havelighanpur | Sivampeta | Nizampeta |
| 3 | Papannapeta | Koudipalli | Yeldurthi |
| 4 | Sankarampeta | Kulcharam | Chegunta |
| 5 | Tekmal | Chilpched | Narsingi |
| 6 | Alladurg | Tupran | |
| 7 | Regodu | Anantasagar | Manoharabad |
References[edit]
- ↑ "Profile". Medak District. Retrieved 14 February 2014.
- ↑ Murty, M. L. K. (2003). Comprehensive History and Culture of Andhra Pradesh: Pre- and protohistoric ... - Google Books. ISBN 9788125024750. Retrieved 14 February 2014.
- ↑ v ramchandra rao. "Prehistoric rock art near Hyderabad, India". Indculture0.tripod.com. Retrieved 14 February 2014.
- ↑ During the era of Qutub Shahis this was named as Gulshanabad due to its vegetation and gardens. later it was again changed to Medak district. http://www.thehindu.com/todays-paper/tp-national/tp-andhrapradesh/treasuring-the-prehistoric-rock-art/article2046635.ece
- ↑ 5.0 5.1 5.2 "New districts". Andhra Jyothy.com. 8 October 2016. Retrieved 8 October 2016.
- ↑ 6.0 6.1 Ministry of Panchayati Raj (8 September 2009). "A Note on the Backward Regions Grant Fund Programme" (PDF). National Institute of Rural Development. Archived from the original (PDF) on 5 April 2012. Retrieved 27 September 2011.
- ↑ "K Chandrasekhar Rao appoints collectors for new districts". Deccan Chronicle. 11 October 2016. Retrieved 13 October 2016.
- ↑ "Clipping of Andhra Jyothy Telugu Daily – Hyderabad". Andhra Jyothy. Retrieved 8 October 2016.