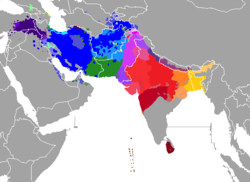
Indo-Iranian languages
This article needs additional citations for verification. (December 2019) |
| Indo-Iranian | |
|---|---|
| Aryan | |
| Geographic distribution | South, Central, Western Asia, South East Europe and the Caucasus / Total speakers = approximately 1.5 billion in 15 countries |
| Linguistic classification | Indo-European
|
| Proto-language | Proto-Indo-Iranian |
| Subdivisions | |
| ISO 639-5 | iir |
| Glottolog | indo1320 |
 The approximate present-day distribution of the Indo-European branches of Eurasia:
Indo-Iranian | |
The Indo-Iranian languages (also Indo-Iranic languages[1][2] or Aryan languages[3]) constitute the largest and southeasternmost extant branch of the Indo-European language family. They have more than 1.5 billion speakers, stretching from Europe (Romani), Turkey (Kurdish and Zaza–Gorani) and the Caucasus (Ossetian) eastward to Xinjiang (Sarikoli) and Assam (Assamese), and south to Sri Lanka (Sinhala) and the Maldives (Maldivian), with branches stretching as far out as Oceania and the Caribbean for Fiji Hindi and Caribbean Hindustani respectively. Furthermore, there are large diaspora communities of Indo-Iranian speakers in northwestern Europe (the United Kingdom), North America (United States, Canada), Australia, South Africa, and the Persian Gulf Region (United Arab Emirates, Saudi Arabia).
The common ancestor of all of the languages in this family is called Proto-Indo-Iranian—also known as Common Aryan—which was spoken in approximately the late 3rd millennium BC. The three branches of the modern Indo-Iranian languages are Indo-Aryan, Iranian, and Nuristani. A fourth independent branch, Dardic, was previously posited, but recent scholarship in general places Dardic languages as archaic members of the Indo-Aryan branch.[4]
Languages[edit | edit source]
The Indo-Iranian languages consist of three groups:
Indo-Iranian languages are spoken by more than 1.5 billion people. The languages with the most speakers are a part of the Indo-Aryan group: Hindi–Urdu (~590 million[5]) - the Indian census having often included Bhojpuri (40 million), Awadhi (40 million), Maithili (35 million), Marwari (30 million), Rajasthani (20 million), Chhattisgarhi (18 million) and Kumaoni (2.1 million) as dialects - Bengali (205 million[6]), Punjabi (100 million), Marathi (90 million), Gujarati (50 million), Odia (35 million), Sindhi (25 million), Assamese (24 million), Sinhala (19 million), Nepali (17 million), Bishnupuriya (12 million)[7] and Rangpuri (15 million). Among the Iranian branch, major languages are Persian (90 million),[8] Pashto (ca. 70 million), Kurdish (35 million),[9] and Balochi (8 million). There are also many smaller languages.
| Part of a series on |
| Indo-European topics |
|---|
 |
History[edit | edit source]
This section needs expansion. You can help by adding to it. (December 2018) |
The common proto-language of the Indo-Iranian languages is the Proto-Indo-Iranian language, which has been reconstructed.
The oldest attested Indo-Iranian languages are Vedic Sanskrit, Older and Younger Avestan and Old Persian (ancient Iranian languages). A few words from another Indo-Aryan language (see Indo-Aryan superstrate in Mitanni) are attested in documents from the ancient Mitanni and Hittite kingdoms in the Near East.
Within the Indo-European family, Indo-Iranian belongs to the Satem group. Various proposals have been made that link the Indo-Iranian languages with other subgroups of Indo-European (like Graeco-Aryan, which posits a close relationship with Greek and Armenian), but these remain without wider acceptance.
Features[edit | edit source]
Innovations shared with other languages affected by the satem sound changes include:[citation needed]
- Fronting and assibilation of the Proto-Indo-European (PIE) palato-velar stops: Template:PIE
- The merger of the PIE labiovelar and plain velar stops: Template:PIE
- The Ruki sound law
Innovations shared with Greek include:[citation needed]
- The vocalization of the PIE syllabic nasals Template:PIE to Template:PIE (may be independent developments)
- Grassmann's law (may be independent developments)
Innovations unique to Indo-Iranian include:[citation needed]
- The lowering of PIE Template:PIE to Template:PIE
- *o was also lowered to *a, though this occurred in several other Indo-European languages as well.
- The PIE laryngeal Template:PIE between consonants became Template:PIE, though it was apparently reduced to zero in Iranian.
- The use of a verb root *kr̥- to derive verbal forms from nouns.
- The use of *-yá- to derive passive verbs from roots.
- Brugmann's law
References[edit | edit source]
- ↑ D. D. Mahulkar (1990). Pre-Pāṇinian Linguistic Studies. Northern Book Centre. ISBN 978-81-85119-88-5.
- ↑ Annarita Puglielli; Mara Frascarelli (2011). Linguistic Analysis: From Data to Theory. Walter de Gruyter. ISBN 978-3-11-022250-0.
- ↑ Jadranka Gvozdanović (1999). Numeral Types and Changes Worldwide. Walter de Gruyter. p. 221. ISBN 978-3-11-016113-7.: "The usage of 'Aryan languages' is not to be equated with Indo-Aryan languages, rather Indo-Iranic languages of which Indo-Aryan is a subgrouping."
- ↑ Bashir, Elena (2007). Jain, Danesh; Cardona, George (eds.). The Indo-Aryan languages. p. 905. ISBN 978-0415772945.
'Dardic' is a geographic cover term for those Northwest Indo-Aryan languages which [..] developed new characteristics different from the IA languages of the Indo-Gangetic plain. Although the Dardic and Nuristani (previously 'Kafiri') languages were formerly grouped together, Morgenstierne (1965) has established that the Dardic languages are Indo-Aryan, and that the Nuristani languages constitute a separate subgroup of Indo-Iranian.
- ↑ Edwards, Viv. "Urdu Today". BBC.
- ↑ Thompson, Irene. "Bengali". AboutWorldLanguages. Retrieved 29 March 2013.
- ↑ "Census of India: Family-wise grouping of the 122 Scheduled and Non-Scheduled Languages -2001". www.censusindia.gov.in.
- ↑ Noack, Rick. "The future of language". Washington Post. Retrieved 27 March 2020.
- ↑ CIA- The World Factbook: 14.7 million in Turkey (18%)[1][failed verification], 4.9–6.5 million in Iraq (15-20%)[2][failed verification], 8 million in Iran (10%)"Archived copy". Retrieved 31 March 2011.[failed verification] (all for 2014), plus several million in Syria, neighboring countries, and the diaspora
Sources[edit | edit source]
- Chakrabarti, Byomkes (1994). A comparative study of Santali and Bengali. Calcutta: K.P. Bagchi & Co. ISBN 81-7074-128-9
- Nicholas Sims-Williams, ed. (2002). Indo-Iranian Languages and Peoples. Oxford University Press.
Further reading[edit | edit source]
- "Contact and change in the diversification of the Indo-Iranic languages" (PDF). Dr. Russell Gray.
- Pinault, Georges-Jean. "Contacts religieux et culturels des Indo-Iraniens avec la civilisation de l'Oxus". In: Comptes rendus des séances de l'Académie des Inscriptions et Belles-Lettres, 149ᵉ année, N. 1, 2005. pp. 213–257. DOI:https://doi.org/10.3406/crai.2005.22848 ; www.persee.fr/doc/crai_0065-0536_2005_num_149_1_22848
- Pinault, Georges-Jean. "La langue des Scythes et le nom des Arimaspes". In: Comptes rendus des séances de l'Académie des Inscriptions et Belles-Lettres, 152e année, N. 1, 2008. pp. 105–138. DOI:https://doi.org/10.3406/crai.2008.92104 ; www.persee.fr/doc/crai_0065-0536_2008_num_152_1_92104
- Baly, Joseph. Eur-Aryan roots: With their English derivatives and the corresponding words in the cognate languages compared and systematically arranged. Vol. 1. K. Paul, Trench, Trubner & Company, Limited, 1897.
External links[edit | edit source]
- Swadesh lists of Indo-Iranian basic vocabulary words (from Wiktionary's Swadesh-list appendix)
Template:Indo-European languages
Template:Indo-Iranian languages