Himachal Pradesh Legislative Assembly
Himachal Pradesh Legislative Assembly | |
|---|---|
| 13th Legislative Assembly of Himachal Pradesh | |
| Type | |
| Type | |
Term limits | 5 years |
| Leadership | |
Speaker | |
Deputy Speaker | |
Leader of the House (Chief Minister) | |
Leader of the Opposition | |
| Structure | |
| Seats | 68 |
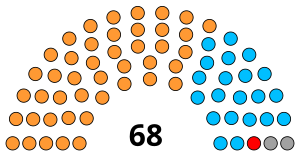 | |
Political groups | Government (43)
Opposition (19)
Others (3) Vacant (3)
|
| Elections | |
| First past the post | |
Last election | 9 November 2017 |
Next election | November 2022 |
| Meeting place | |
 | |
| Himachal Pradesh Legislative Assembly, Shimla, Himachal Pradesh, India[1] | |
| Website | |
| Himachal Pradesh Legislative Assembly | |
The Himachal Pradesh Legislative Assembly or the Himachal Pradesh Vidhan Sabha is the unicameral legislature of the Indian state of Himachal Pradesh.[2] The present strength of the Vidhan Sabha is 68. Himachal Pradesh is the first state in India to launch paperless legislative assembly .[3][4] The Vidhan Sabha building located above Nabha. The building comes under Annadale Political Ward, i.e. Ward - 4 of Shimla Municipal Corporation.
History
The Himachal Pradesh Legislative Assembly was created after Independence. It first sine into existence as a centrally administered territory on 15th April, 1948 by the integration of 30 erstwhile Princely States (26 Shimla hill states and 4 Punjab hill states). In 1952, the state became a Part 'C'state under the Section 3 of Part 'C' State's Act, 1951, the state was brought under a Lt Governor with 36 members, including 2 nominated members in Legislative Assembly. First election to the Assembly were held in 1952. Bilaspur once a Part 'C' state, was merged with Himachal Pradesh in 1954 and the strength of the Assembly was raised to 41 members.
On 1st November, 1956, Himachal Pradesh was made a Union Territory. Finally in 1963, Parliament has passed a bill for the system of Council of Ministers and an Assembly for Himachal Pradesh. The bill received President's assent on 1st July, 1963 and came into force. Then, the Territorial Council converted into a Legislative Assembly of the Union Territory of Himachal Pradesh.
Thus, the Assembly was constituted on 1st July, 1963 and it was called the first Legislative Assembly. On 1st October, 1963, the Legislative Assembly held its first sitting but its membership was raised in 1966, when new areas were merged into Himachal Pradesh
List of assemblies
Power and Function
Legislative Powers
The main function of the Legislative Assembly is to make laws. But power make laws is confined to the State List and the Concurrent List.
Financial Powers
The Money Bill is introduced only in the Legislative Assembly. The assembly is required to pass the demand for grants and tax raising proposals. No money can be spent from the state treasury without the authority of the Legislative Assembly.
Control over Executive
The ministers are collectively responsible to the Legislative Assembly. They will be forced to resign if a no-confidence motion is passed by the Legislative Assembly
Officers of Legislative Assembly
Speaker of the Legislative Assembly of Himachal Pradesh
Speaker is the head of Legislative Assembly. All the proceedings in the house are conducted under his guardianship. In his absence, this role is played by Deputy Speaker. Shri Jaiwant Ram was the first Speaker and Shri Krishan Chander was the first Deputy Speaker of the Legislative Assembly of Himachal Pradesh.
Himachal Pradesh Legislature Secretariat
The Legislative Assembly Secretariat, provide secretarial assistance in Legislative functioning of the Hon'ble Speaker. It also fulfills the requirements of the members of Legislative Assembly for ensuring timely assistance in the discharge of their functions.
The Legislative Secretariat also takes care of the welfare of the members and er-members. The service conditions of employees of Himachal Pradesh Legislature Secretariat are governed under the Himachal Pradesh Vidhan Sabha Secretariat Rules, 1974.
The Legislature Secretariat does not implement schemes directly. Therefore, the work of the Legislature Secretariat is completely different from that of other Government departments and the State Secretariat.
Powers and Duties of Legislature Secretariat
The officers and staff of the Secretariat are assigned with duties to serve the House. the Speaker, the Deputy Speaker and the members of the Legislative Assembly. The Secretary of the Legislative Assembly exercises all the powers of the Secretary to the Government, both administrative and financial as conferred by the State Government from time-to-time.
In the assembly, all the administrative and financial sanctions are issued in the name of the Speaker and these sanctions are authenticated by the Secretary. The Executive and financial orders issued by the government from time-to-time are not automatically applied to Himachal Pradesh Vidhan Sabha Secretariat, but are made applicable after due examination and approval of the Speaker.
Current party composition
Template:Party name with colourTemplate:Party name with colourTemplate:Party name with colourTemplate:Party name with colourTemplate:Party name with colour| Party | Members | |
|---|---|---|
| 43 | ||
| 19 | ||
| 1 | ||
| 2 | ||
| 3 | ||
| Total | 68 | |
.
List of Members of the Himachal Legislative Assembly
See also
References
- ↑ "Himachal Pradesh Cabinet to discuss venue of upcoming Himachal Pradesh Legislative Assembly's session". theindianexpress.com.
- ↑ Himachal Legislative Assembly
- ↑ "India gets its first paperless as Himachal Pradesh Legislative Assembly also known as e-Vidhan". theindianexpress.com.
- ↑ "India's first digital or e-vidhansabha assembly in Himachal Pradesh". Amar Ujala.
