IRNSS-1G: Difference between revisions
>Niterurea (Added photo) |
m (Removed empty portal template using script) |
||
| (One intermediate revision by one other user not shown) | |||
| Line 52: | Line 52: | ||
}} | }} | ||
''' | '''IRNSS-1G''' was the seventh and final<ref name="Launch" /> of the [[Indian Regional Navigation Satellite System]] (IRNSS) series of satellites after [[IRNSS-1A]], [[IRNSS-1B]], [[IRNSS-1C]], [[IRNSS-1D]], [[IRNSS-1E]] and [[IRNSS-1F]]. This system of satellites will provide navigational services to the Indian region. The satellite was launched successfully on 28 April 2016 at 07:20 UTC.<ref name="Launch" /> | ||
IRNSS-1G along IRNSS-1A is being used only for NavIC's short message broadcast service and not for navigation.<ref name=":11">{{cite web|title=Annual Report 2019-20|url=https://www.isro.gov.in/sites/default/files/flipping_book/annual_report_2019-20_english/index.html#50|access-date=5 March 2020|publisher=Department of Space}}</ref><ref name="ar-2021">{{cite web|title=ANNUAL REPORT 2020-2021|url=https://www.isro.gov.in/sites/default/files/anual_report_2020-2021_english.pdf|access-date=6 March 2021|publisher=ISRO}}</ref> | |||
== Launch == | == Launch == | ||
The satellite was launched from the [[Satish Dhawan Space Centre First Launch Pad|First Launch Pad (FLP)]] of [[Satish Dhawan Space Centre]], [[Sriharikota]] on board [[Polar Satellite Launch Vehicle|PSLV-C33]].<ref name="Launch">{{Cite news|url =http://www.thehindu.com/sci-tech/science/irnss-launch-indias-own-regional-navigation-satellite-system-takes-shape/article8531388.ece|title = India launches seventh navigation satellite, to get its own GPS |date = April 28, 2016|work = The Hindu|access-date = April 28, 2016}}</ref> The countdown of the launch had begun 51:30 hours before at 9:20 | The satellite was launched from the [[Satish Dhawan Space Centre First Launch Pad|First Launch Pad (FLP)]] of [[Satish Dhawan Space Centre]], [[Sriharikota]] on board [[Polar Satellite Launch Vehicle|PSLV-C33]] XL on 28 April 2016 at 12:50 PM [[Indian Standard Time|IST]].<ref name="Launch">{{Cite news|url =http://www.thehindu.com/sci-tech/science/irnss-launch-indias-own-regional-navigation-satellite-system-takes-shape/article8531388.ece|title = India launches seventh navigation satellite, to get its own GPS |date = April 28, 2016|work = The Hindu|access-date = April 28, 2016}}</ref><ref>{{cite web|title=PSLV-C33/IRNSS-1G|url=http://www.isro.gov.in/launcher/pslv-c33-irnss-1g|access-date=28 April 2016|publisher=ISRO}}</ref> The countdown of the launch had begun 51:30 hours before at 9:20 AM IST on 25 April 2016.<ref name="countdown" /> | ||
After the launch of IRNSS-1G the Indian government named the IRNSS system as NAVIC (Navigation | After the launch of IRNSS-1G the Indian government named the IRNSS system as NAVIC ('''Nav'''igation with '''I'''ndian '''C'''onstellation).<ref>{{Cite web|title=PSLV-C33 Successfully Launches India's Seventh Navigation Satellite IRNSS-1G - ISRO|url=https://www.isro.gov.in/update/28-apr-2016/pslv-c33-successfully-launches-indias-seventh-navigation-satellite-irnss-1g|access-date=2021-11-01|website=www.isro.gov.in}}</ref> | ||
== Specifications == | == Specifications == | ||
'''Mission life:''' 12 years (planned).<ref name="countdown">{{cite web | url=http://www.thehindubusinessline.com/news/science/countdown-for-irnss1g-launch-begins-at-sriharikota/article8523638.ece | title=Countdown for IRNSS-1G launch begins at Sriharikota | work=[[The Hindu]] | date=26 April 2016 | access-date=28 April 2016 | author=PTI}}</ref> | |||
"Spec">{{cite web | url=http://www.isro.gov.in/sites/default/files/pslv-c33_brochure.pdf | title=PSLV-C33 - IRNSS-1G Specifications | publisher=ISRO | access-date=28 April 2016}}</ref> | |||
'''Lift-off mass:'''{{Convert|1425|kg}} | |||
'''Dry mass:''' {{Convert|598|kg}}.<ref name="Spec">{{cite web | url=http://www.isro.gov.in/sites/default/files/pslv-c33_brochure.pdf | title=PSLV-C33 - IRNSS-1G Specifications | publisher=ISRO | access-date=28 April 2016}}</ref> | |||
'''Payload:''' [[Code-division multiple access|CDMA]] ranging payload in [[C band (IEEE)|C band]].<ref>{{Cite news|url =http://www.business-standard.com/article/current-affairs/isro-launches-rocket-carrying-india-s-seventh-navigation-satellite-116042800308_1.html|title = 'Isro launches rocket carrying India's seventh navigation satellite'|date = April 28, 2016|work = Business Standard|access-date = April 28, 2016}}</ref><ref name=":0">{{Cite web|title=SALIENT FEATURES OF IRNSS 1G|url=https://www.ursc.gov.in/navigation/html/irnss-1g.jsp|access-date=2021-11-01|website=www.ursc.gov.in}}</ref> Navigation payload in [[L band|L-5]] and [[S band]] spectrums and [[Rubidium atomic clock|Rubidium atomic clocks]].<ref>{{cite web | url=http://www.isro.gov.in/Spacecraft/irnss-1g | title=IRNSS-1G | work=ISRO | access-date=28 April 2016}}</ref> | |||
'''Power:''' Two [[Multi-junction solar cell|triple-junction solar panels]] to generate 1660W of energy and one Lithium-ion 90A-hr battery is used.<ref name="Spec" /> | |||
'''Propulsion:''' [[Monomethylhydrazine|MMH]]/[[Mixed oxides of nitrogen|MON3]] based bipropellant system with 12×22N [[Attitude control]] thrusters and one 440N [[Liquid apogee engine|LAM]].<ref name=":0" /> | |||
'''Orbit:''' [[Geosynchronous orbit]] at 129.5° East longitude with 5° inclination.<ref name="Spec" /><ref>{{cite web | url=http://indiatoday.intoday.in/story/indias-own-navigation-satellite-irnss-1g-launched-all-you-need-to-know-about-it/1/653698.html | title=India's own navigation satellite IRNSS-1G launched: All you need to know about it | work=[[India Today]] | date=28 April 2016 | access-date=28 April 2016 | author=Sangeeta Ojha}}</ref> | |||
'''Cost:''' Approximately {{INRConvert|125|c}}.<ref name="Desi">{{cite web | url=http://economictimes.indiatimes.com/news/science/irnss-desi-gps-to-liberate-india-from-dependence-on-us-russia/articleshow/52058262.cms | title=IRNSS: Desi GPS to liberate India from dependence on US, Russia | work=Economic Times | date=1 May 2016 | access-date=2 May 2016 | author=Vanita Srivastava}}</ref> | |||
{{multiple image | {{multiple image | ||
| Line 80: | Line 93: | ||
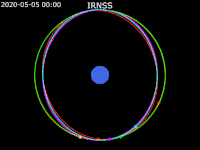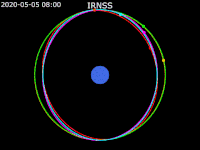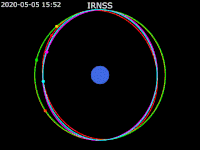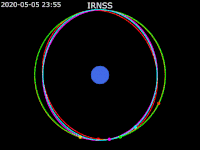
| image5 = Animation of IRNSS orbit - Earth fixed - polar view.gif | | image5 = Animation of IRNSS orbit - Earth fixed - polar view.gif | ||
| caption5 = [[ECEF|Earth fixed frame]] - Polar view | | caption5 = [[ECEF|Earth fixed frame]] - Polar view | ||
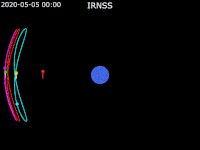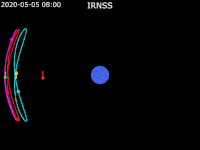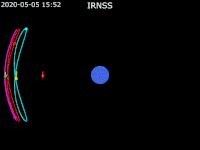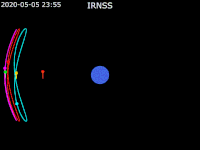
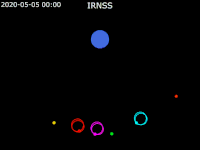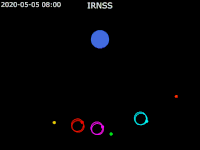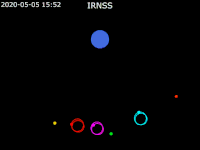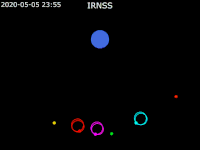
| footer = {{legend2| RoyalBlue | Earth}}{{·}}{{legend2| magenta |[[IRNSS-1B]] }}{{·}}{{legend2| lime |[[IRNSS-1C]] }}{{·}}{{legend2| Cyan |[[IRNSS-1E]] }}{{·}}{{legend2|Gold|[[IRNSS-1F]] }}{{·}}{{legend2| OrangeRed| | | footer = {{legend2| RoyalBlue | Earth}}{{·}}{{legend2| magenta |[[IRNSS-1B]] }}{{·}}{{legend2| lime |[[IRNSS-1C]] }}{{·}}{{legend2| Cyan |[[IRNSS-1E]] }}{{·}}{{legend2|Gold|[[IRNSS-1F]] }}{{·}}{{legend2| OrangeRed|IRNSS-1G }}{{·}}{{legend2| Red|[[IRNSS-1I]]}} | ||
}} | }} | ||
{{clear}} | {{clear}} | ||
==See also== | ==See also== | ||
* [[Communication-Centric Intelligence Satellite|Communication-Centric Intelligence Satellite (CCI-Sat)]] | * [[Communication-Centric Intelligence Satellite|Communication-Centric Intelligence Satellite (CCI-Sat)]] | ||
* [[GPS-aided geo-augmented navigation|GPS-aided geo-augmented navigation (GAGAN)]] | * [[GPS-aided geo-augmented navigation|GPS-aided geo-augmented navigation (GAGAN)]] | ||
Latest revision as of 07:02, 14 August 2023
 | |
| Mission type | Navigation |
|---|---|
| Operator | ISRO |
| COSPAR ID | {{#property:P247}} |
| SATCAT no. | 41469 |
| Mission duration | 12 years |
| Spacecraft properties | |
| Spacecraft | IRNSS-1G |
| Spacecraft type | Satellite |
| Bus | I-1K |
| Manufacturer | ISRO Satellite Centre Space Applications Centre |
| Launch mass | 1,425 kilograms (3,142 lb) |
| Dry mass | 598 kilograms (1,318 lb) |
| Power | 1600 W |
| Start of mission | |
| Launch date | 12:50:00, April 28, 2016 (UTC+05:30) |
| Rocket | PSLV-XL C33 |
| Launch site | Satish Dhawan (First) |
| Contractor | ISRO |
| Orbital parameters | |
| Reference system | Geocentric |
| Regime | Geosynchronous Orbit (GSO) |
| Longitude | 129.429213 East |
| Perigee altitude | 35,780.961 km (22,233.258 mi)[1] |
| Apogee altitude | 35,796.200 km (22,242.727 mi)[1] |
| Inclination | 4.2637 |
| Period | 23:56:12.33 |
| Epoch | 17151.68965311 |
IRNSS-1G was the seventh and final[2] of the Indian Regional Navigation Satellite System (IRNSS) series of satellites after IRNSS-1A, IRNSS-1B, IRNSS-1C, IRNSS-1D, IRNSS-1E and IRNSS-1F. This system of satellites will provide navigational services to the Indian region. The satellite was launched successfully on 28 April 2016 at 07:20 UTC.[2]
IRNSS-1G along IRNSS-1A is being used only for NavIC's short message broadcast service and not for navigation.[3][4]
Launch[edit]
The satellite was launched from the First Launch Pad (FLP) of Satish Dhawan Space Centre, Sriharikota on board PSLV-C33 XL on 28 April 2016 at 12:50 PM IST.[2][5] The countdown of the launch had begun 51:30 hours before at 9:20 AM IST on 25 April 2016.[6]
After the launch of IRNSS-1G the Indian government named the IRNSS system as NAVIC (Navigation with Indian Constellation).[7]
Specifications[edit]
Mission life: 12 years (planned).[6]
Lift-off mass:1,425 kilograms (3,142 lb)
Dry mass: 598 kilograms (1,318 lb).[8]
Payload: CDMA ranging payload in C band.[9][10] Navigation payload in L-5 and S band spectrums and Rubidium atomic clocks.[11]
Power: Two triple-junction solar panels to generate 1660W of energy and one Lithium-ion 90A-hr battery is used.[8]
Propulsion: MMH/MON3 based bipropellant system with 12×22N Attitude control thrusters and one 440N LAM.[10]
Orbit: Geosynchronous orbit at 129.5° East longitude with 5° inclination.[8][12]
Cost: Approximately ₹125 crore (US$14 million).[13]
See also[edit]
- Communication-Centric Intelligence Satellite (CCI-Sat)
- GPS-aided geo-augmented navigation (GAGAN)
- Satellite navigation
References[edit]
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 "NORAD Catalog Number 41469". NORAD. Retrieved 2 June 2017.
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 2.2 "India launches seventh navigation satellite, to get its own GPS". The Hindu. 28 April 2016. Retrieved 28 April 2016.
- ↑ "Annual Report 2019-20". Department of Space. Retrieved 5 March 2020.
- ↑ "ANNUAL REPORT 2020-2021" (PDF). ISRO. Retrieved 6 March 2021.
- ↑ "PSLV-C33/IRNSS-1G". ISRO. Retrieved 28 April 2016.
- ↑ 6.0 6.1 PTI (26 April 2016). "Countdown for IRNSS-1G launch begins at Sriharikota". The Hindu. Retrieved 28 April 2016.
- ↑ "PSLV-C33 Successfully Launches India's Seventh Navigation Satellite IRNSS-1G - ISRO". www.isro.gov.in. Retrieved 1 November 2021.
- ↑ 8.0 8.1 8.2 "PSLV-C33 - IRNSS-1G Specifications" (PDF). ISRO. Retrieved 28 April 2016.
- ↑ "'Isro launches rocket carrying India's seventh navigation satellite'". Business Standard. 28 April 2016. Retrieved 28 April 2016.
- ↑ 10.0 10.1 "SALIENT FEATURES OF IRNSS 1G". www.ursc.gov.in. Retrieved 1 November 2021.
- ↑ "IRNSS-1G". ISRO. Retrieved 28 April 2016.
- ↑ Sangeeta Ojha (28 April 2016). "India's own navigation satellite IRNSS-1G launched: All you need to know about it". India Today. Retrieved 28 April 2016.
- ↑ Vanita Srivastava (1 May 2016). "IRNSS: Desi GPS to liberate India from dependence on US, Russia". Economic Times. Retrieved 2 May 2016.