Ghent Kangri
Thank you for being part of the Bharatpedia family! 0% transparency: ₹0 raised out of ₹100,000 (0 supporter) |
| Ghent Kangri | |
|---|---|
| Mount Ghent | |
Lua error in Module:Location_map at line 501: Unable to find the specified location map definition: "Module:Location map/data/Karakoram relief" does not exist.
| |
| Highest point | |
| Elevation | 7,401 m (24,281 ft) Ranked 69th |
| Prominence | 1,493 m (4,898 ft) |
| Coordinates | 35°31′39″N 76°48′39″E / 35.52750°N 76.81083°ECoordinates: 35°31′39″N 76°48′39″E / 35.52750°N 76.81083°E |
| Geography | |
| Location | Saltoro Ridge, Siachen, near the Actual Ground Position Line (the line between Indian and Pakistan controlled territories)[1][2][3] |
| Parent range | Saltoro Mountains, Karakoram |
| Climbing | |
| First ascent | 1961 by Wolfgang Axt (Austrian) |
| Easiest route | West Ridge: glacier/snow climb |
Ghent Kangri (or Mount Ghent, Ghaint I) is a high peak near the north end of the Saltoro Mountains, a subrange of the Karakoram range. It is located west of the Siachen Glacier near the Actual Ground Position Line between India and Pakistan.
Ghent Kangri was first climbed on 4 June 1961, by Wolfgang Axt, a member of an Austrian expedition led by Erich Waschak, via the West Ridge. He climbed solo above the high camp.
According to the Himalayan Index, there have been three subsequent ascents of the peak, in 1977, 1980, and 1984.
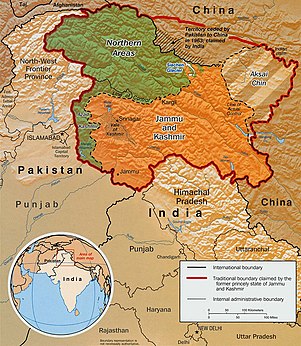
Indo-Pak mutually-agreed undisputed "International Border" (IB) in the black line, Indo-Pak "Line of Control" (LoC) in black dotted line in the north and west, Indo-Sino "Line of Actual" (LAC) in black dotted line in the east, Indo-Pak line across Siachen in north is "Actual Ground Position Line" (AGPL). The areas shown in green are the two Pakistani-controlled areas: Gilgit–Baltistan in the north and Azad Kashmir in the south. The area shown in orange is the Indian-controlled territories of Jammu and Kashmir, and Ladakh, and the diagonally-hatched area to the east is the Chinese-controlled area known as Aksai Chin. "Territories ceded by Pakistan to China claimed by India" in the north is Shaksgam (Trans-Karakoram Tract).

United Nations map of Siachen Glacier showing "Point NJ980420" (Point NJ9842) as starting point of "Actual Ground Position Line" (AGPL), Goma military camp of Pakistan, Nubra River valley and Siachen glaciers held by India; Bilafond La and Sia La north of NJ9842 are also held by India. Masherbrum Range, Baltoro Glacier, Baltoro Glacier, Baltoro Muztagh and K2 are held by Pakistan.
See also[edit]
- Near the AGPL (Actual Ground Position Line)
- NJ9842, LoC ends and AGPL begins
- Gyong La
- Chumik Glacier
- Saltoro Mountains
- Saltoro Kangri
- Bilafond La
- Sia La
- Indira Col, AGPL ends at LAC
- Borders
- Actual Ground Position Line (AGPL)
- India–Pakistan International Border {IB)
- Line of Control {LoC)
- Line of Actual Control (LAC)
- Sir Creek (SC)
- Borders of China
- Borders of India
- Borders of Pakistan
- Conflicts
- Kashmir conflict
- Siachen conflict
- Sino-Indian conflict
- List of disputed territories of China
- List of disputed territories of India
- List of disputed territories of Pakistan
- Northern Areas
- Trans-Karakoram Tract
- Operations
- Operation Meghdoot, by India
- Operation Rajiv, by India
- Operation Safed Sagar, by India
- Other related topics
- Awards and decorations of the Indian Armed Forces
- Bana Singh, after whom Quaid Post was renamed to Bana Top
- Dafdar, westernmost town in Trans-Karakoram Tract
- India-China Border Roads
- Sino-Pakistan Agreement for transfer of Trans-Karakoram Tract to China
References[edit]
- ↑ The Future of Kashmir on the BBC website.
- ↑ Peak Ghent Kangri, Diskit Nubra, Leh District, Ladakh, India, OpenStreetMap, retrieved 30 May 2020.
- ↑ "Ghent Kangri, Pakistan/India". Peakbagger.com. Retrieved 29 December 2020.
Sources[edit]
- Neate, Jill (1989). High Asia: an illustrated history of the 7,000 metre peaks. The Mountaineers.
- Jerzy Wala, Orographical Sketch Map of the Karakoram, Swiss Foundation for Alpine Research, 1990.
