Afghan–Maratha War
The Afghan–Maratha War was fought between the Afghan Empire under Ahmad Shah Durrani and the Maratha Confederacy and the Sikh Confederacy between 1758 and 1761.[1] It took place in north-west India, primarily the region around Delhi and Punjab.[2]. The war was continued by the Rohilla Afghans and Taimur Shah Durrani till 1790.
| Afghan–Maratha War | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Part of the Indian campaign of Ahmad Shah Durrani | |||||||
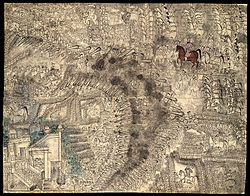 Third Battle of Panipat, 14 January 1761 | |||||||
| |||||||
| Belligerents | |||||||
Afghan Empire
|
Sikh Confederacy | ||||||
| Commanders and leaders | |||||||
Background
Pathan War and Marathas
In April 1751, a Bangash incursion into northern India was repelled at Qadirganj. When the Rohilla Pathans advanced to support their Sunni allies, they encountered strong resistance near Farrukhabad from Maratha forces led by Gangadhar Jaswant and Jawahir Singh Jat. The engagement resulted in a decisive defeat for the Rohillas: their commander, Sadulla Khan, retreated from the battlefield, while Bahadur Khan was killed. Reports suggest that around 10,000 Rohilla fighters perished in the battle, forcing the invaders to withdraw across the Ganges on 28 April.
Ahmad Shah Durrani
In 1757, the Afghans invaded Hindustan and captured the Mughal capital of Delhi, forcing the Mughal emperor to cede territories up till the Sutlej to the Afghan Empire. Delhi was placed under the occupation of an Afghan vassal, the Kingdom of Rohilkhand. The Afghan emperor, Ahmad Shah Durrani installed his son Timur Shah Durrani in Multan and returned to Afghanistan.[2]
Battle of Delhi (1757)
The Mughal emperor and the imperial grand vizier alarmed by this foreign occupation, secretly sent for his vassal, the Peshwa. The Maratha Peshwa Balaji Baji Rao sent his brother Raghunath Rao along with Shamsher Bahadur, Ramsingha, Gangadhar Tatya, Sakharam Bapu Bokil, Naroshankar Rajebahadur, Sidhojiraje Gharge-Desai-Deshmukh, Mankojiraje Gharge-Desai-Deshmukh, Maujiram Bania and a large army towards Delhi. They were accompanied by Malhar Rao Holkar of Malwa who had much experience in North India and with its rulers. The Marathas captured Delhi in August 1757. They decisively defeated the Rohillas near Delhi in 1758.[2]
Reference
- ↑ Kohn, George C. Dictionary of Wars.
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 2.2 War, Culture and Society in Early Modern South Asia, 1740-1849